- Vietnam’s trade background: From a hermit nation to an essential member of world trade
- 1. EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA)
- 2. Comprehensive and Progessive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
- 3. UK – Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
- 4. U.S.-Vietnam Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA)
- 5. ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA)
- 6. ASEAN – China Free Trade Area (ACFTA)
- 7. ASEAN – Australia – New Zealand Free Trade Area (AANZFTA)
- 8. Vietnam – South Korea Free Trade Agreement (VKFTA)
- 9. Vietnam- Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (VJEPA)
- 10. Vietnam and India under ASEAN (AIFTA)
- 11. Vietnam – Eurasian Economic Union (VN-EAEU FTA)
- 12. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)a
- 13. Vietnam – Cuba Trade Agreement
- 14. Vietnam-Chile Free Trade Agreement (VCFTA)
- 15. ASEAN – Hong Kong, China Free Trade Agreement (AHKFTA)
- Upcoming Free Trade Agreements
Vietnam has embraced economic liberalization with great enthusiasm and invested in human and physical capital, both through public investments as well as opening up the economy to foreign investments. Moreover, the country effectively complemented global liberalization with domestic reforms through ease of doing business and deregulation.
Vietnam has signed significant free trade agreements in the last three decades with over 50 nations, including individual-based agreements as well as those signed via economic blocs. This is impactful considering that before the 1990s Vietnam’s economy was completely insular, similar to that of North Korea. For instance, in 1995, Vietnam became a part of the ASEAN free trade area, and in 2007 it joined the WTO, and later signed a free trade agreement with the US, once Vietnam’s fiercest enemy. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to Vietnam’s free trade agreements.
Investing in Vietnam? See Cekindo’s Company Incorporation Services
Vietnam’s trade background: From a hermit nation to an essential member of world trade
In 1986, Vietnam decided to rescue its economy from the failures of a system setup based on communist central planning and bring profound changes to the country. The government introduced a series of political and economic reform policies known as Doi Moi.
Post-implementation of these reform policies, Vietnam’s economy successfully revived itself and steered to become a “socialist-oriented market economy”. As a result, the country has become an integral part of global trade through increased participation in regional and international institutions and agreements such as the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the United Nations (UN).
According to the US Trade Commission, Vietnam joined the WTO as its 150th member in 2007 and pledged to completely abide by the accords set out by the organization on customs valuation, technical trade barriers (TBT), and sanitary and phytosanitary measures (SPS).
Including trading blocs and one-on-one agreements Vietnam is a signatory to the following trade agreements:
1. EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA)
With a motive to bolster trade relations and deepen international integration, a free trade agreement between the European Union and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam was signed in July 2018.
The EU- Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA) is aimed at providing opportunities to shore up the trade volumes, boost the job market and foster economic growth on both sides, through
- Removal of up to 99% of import taxes
- Protecting the interest of investors
- Elimination of bureaucracy and repeating red tapes
- Reduction of trade barriers
- Encourage the use of public procurement markets and services
- Low-risk and safe trades with Vietnam through the enforced agreement
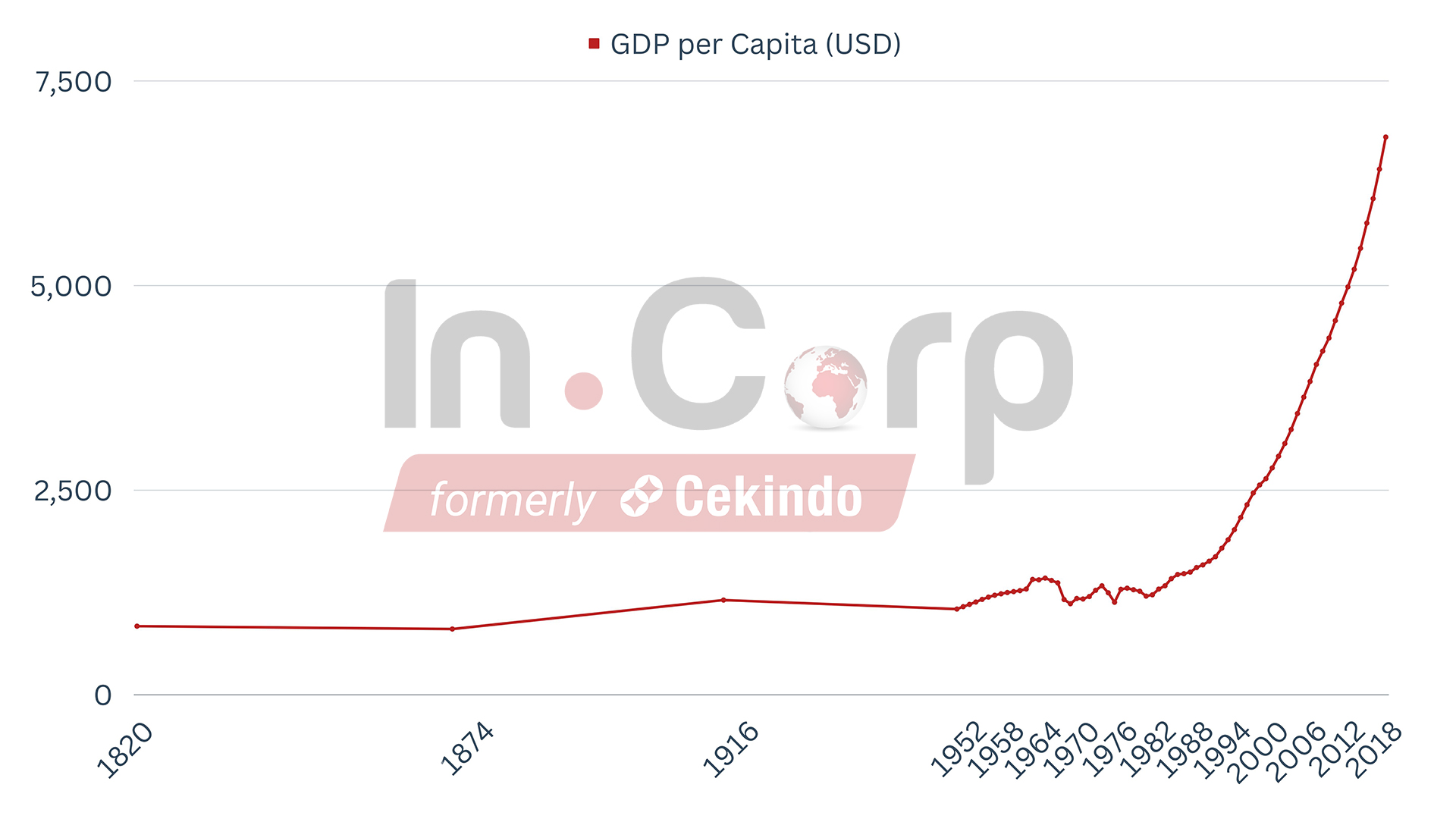
Trade volumes between Vietnam & EU – Source
In fact, as a direct result of the EVFTA, Vietnam’s export surplus to Europe has reached an all-time high of $13.4 billion in the first five months of 2022.
2. Comprehensive and Progessive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
One of the world’s largest free-trade areas, The Comprehensive & Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), consists of 11 signatories representing 13.4% of the global GDP (approximately USD 13.5 trillion). The CPTPP was created after the United States refused to sign the original TPP trade agreement under President Donald Trump (which Vietnam would also have been a member of). The CPTPP includes most of the original member nations excluding the US. The countries participating in the new agreement are:
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Brunei
- Mexico
- Peru
- Chile
- Canada
- Malaysia
- Japan
- Singapore, and
- Vietnam
With the agreement in force, taxes on 43% of Vietnam’s garment exports to Canada will be eliminated with immediate effect, and after four years, they will be slashed by 100%. The agreement also focuses on Vietnam’s labor reforms and improving the work environment. This agreement came into force on the 14th of January 2019 for Vietnam.
3. UK – Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
Between 2011 and 2020, commerce between the UK and Vietnam increased twofold, illustrating a strong bilateral economic partnership and a strategic commitment to international trade. The UK-Vietnam FTA (UKVFTA) not only aims at fostering exchange between the countries but also contains chapters on government procurement, state-owned enterprises, and market competition.
Tariff Elimination under UKFTA
For goods exported by the UK to Vietnam:
- 48.5% of tariffs lines were removed on 01 January 2021;
- 91.8% of tariff lines will be removed by 01 January 2027;
- 98.3% of tariff lines will be removed 01 January 2029;
- 1.7% of tariff lines are partially liberalized through tariff-rate quotas or not entitled to special treatment
For goods imported from Vietnam into the UK:
- 85.6% of tariff lines were removed on 01 January 2021;
- 99.2% of tariff lines will be removed by 01 January 2027;
- 0.8% of tariff lines are partially liberalized through tariff-rate quotas
The agreement also put adequate focus on market liberalization for goods, services, and investments. Moreover, there are commitments relating to sustainable development, labor welfare, and social responsibility.
Vietnam exports to the UK – Source: Trading Economics
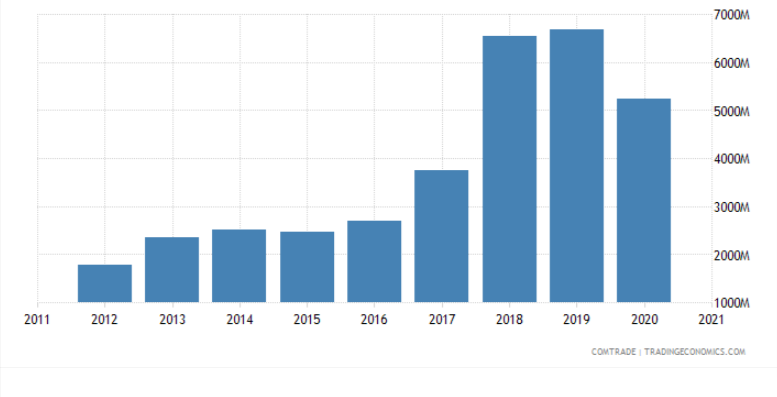
4. U.S.-Vietnam Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA)
In 2020, the trade of goods and services between the US and Vietnam registered USD 92.2 billion (estimated), out of which US exports to Vietnam clocked USD 12.1 billion, whereas imports to the US accounted for USD 80.1 billion.
The U.S.-Vietnam Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) was put into effect to promote freedom to do business and develop across the two countries. The FTA is a thorough pact that addresses issues including commerce in products and services, security of investments, copyright compliance for intellectual property, and incentivization for doing business.
RELATED: Vietnam has Some of the Lowest Operating Costs in Asia
When Vietnam became a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2007, the tariff rates significantly dropped and continued to decrease steadily over the years. Hence, the majority of the exports to the US are only liable for tariffs of 15% or less.
Vietnam’s exports to the US – Source: Trading Economics
5. ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA)
Incepted to boost local trade and manufacturing in all ASEAN countries, the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) is recognized as one of the world’s most significant free trade areas. Moreover, it influenced some of the world’s largest trade forums and blocs, including the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, and East Asia Summit.
AFTA currently consists of the following ten countries:
- Brunei
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Thailand.
- Vietnam
- Laos
- Myanmar
- Cambodia
By removing tariffs and non-tariff obstacles, AFTA is dedicated to transforming ASEAN into a production hub on the international market. For instance:
- The removal of import tariffs on at least 80% of tariff lines;
- e-ASEAN Framework Agreement defines all information and communications technology (ICT) items as exempt from import taxes.
RELATED: Vietnam Business Opportunities 2022
6. ASEAN – China Free Trade Area (ACFTA)
China exported USD 104 billion’s worth of products to Vietnam in 2020, which consisted primarily of telephones, integrated circuits, and pure cotton yarn. Vietnam imported USD 49.4 billion worth of products from China in 2020.
In the year 2000, Leaders of ASEAN and China came together to explore the possibilities of facilitating deeper economic integration within the regions. In the following year, the idea of establishing the ASEAN–China Free Trade Area was endorsed.
Between 2003 and 2008, China experienced a significant increase in trade with ASEAN countries, with trade volume growing from USD 59.6 billion to USD 192.5 billion. Additionally, in 2008, the collective nominal gross GDP of China and ASEAN countries totaled around USD 6 trillion. Two years later, in 2010, the average tariff rates on Chinese goods sold in ASEAN countries decreased from 12.8% to 0.6%, while the tariffs on ASEAN goods sold in China were reduced from 9.8% to 0.1%.
Eventually, the ASEAN–China Free Trade Area transformed into the largest free trade area in terms of population covered and 3rd largest in terms of nominal GDP. In 2015, ASEAN’s total merchandise trade with China registered an impressive USD 346.5 billion.
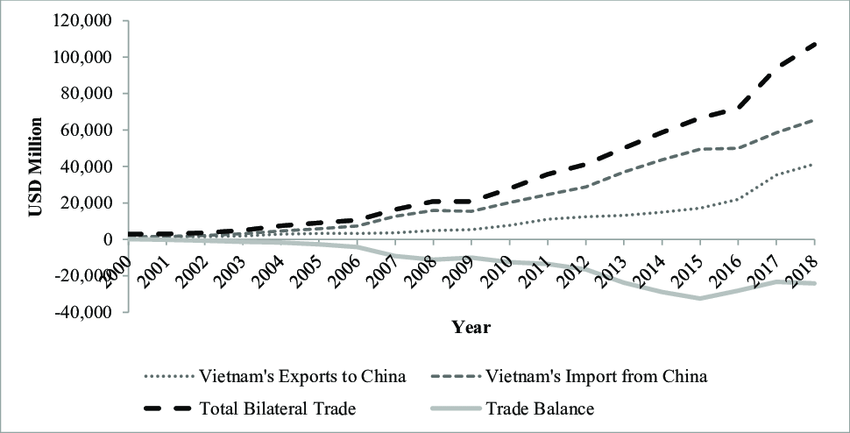
Trade between Vietnam & China. Source: Researchgate
7. ASEAN – Australia – New Zealand Free Trade Area (AANZFTA)
Envisaged to create new opportunities for investors in ASEAN and Australia, and New Zealand, AANZFTA was formed. It is a comprehensive free trade agreement that aims for sustainable economic growth between the two blocks by adopting a transparent and facilitative investment regime. Vietnamese exports to Australia reached USD 3.62 billion before the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, according to United Nations figures. On the other hand, exports from Australia to Vietnam clocked USD 6.23 billion in the first seven months of 2022.
As a result of the AANZFTA, the following can be expected:
- Tariffs will be gradually reduced and eliminated for at least 90% of all tariff lines;
- Enable seamless movement of goods using advanced and flexible rules of origin, streamlined procedures, and more transparent mechanisms;
- Barriers to service trade will be gradually removed, providing service providers in the region greater market access.
- Protecting the interest of investors
8. Vietnam – South Korea Free Trade Agreement (VKFTA)
The Vietnam-Korea free trade agreement (VKFTA), which was established with the goal of boosting bilateral commerce, expanding investment options, and encouraging economic growth, went into force in 2015. Korea has since swiftly risen to the top of foreign investors in Vietnam.
According to the deal, Vietnam will remove 90% of the tariff lines on items imported from South Korea, and South Korea would remove 95% of tariff lines for Vietnam. The agreement also addresses matters including the two nations’ respective approaches to competition law, intellectual property rights, and environmental regulations.
South Korea agreed to let the import of around 500 extra products from Vietnam after the agreement went into force. Additionally, it would lower import taxes on goods including tropical fruits, shrimp, fish, crab, clothing and textiles, and timber goods.
Furthermore, as Vietnam currently hosts close to 3,000 Korean enterprises, the implementation of the VKFTA would contribute to the creation of 400,000+ employment prospects in the nation, according to Mondaq.
Vietnam’s exports to South Korea. Source: TradingEconomics
9. Vietnam- Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (VJEPA)
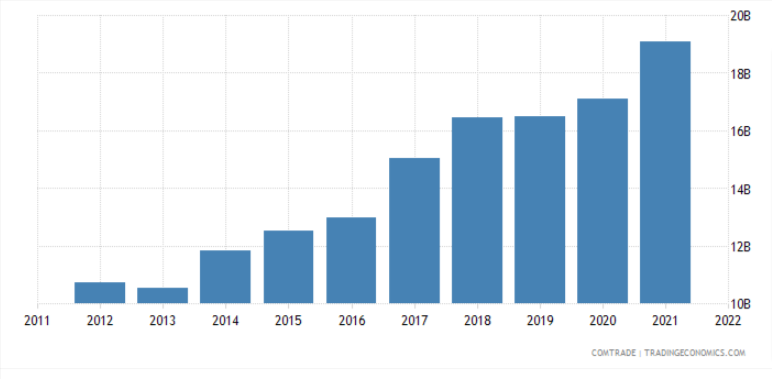
Before the pandemic, Japan’s exports to Vietnam stood at USD 19.11 billion, whereas exports from Vietnam to Japan were USD 21.2 billion. Exports to Vietnam majorly consisted of insulated wire, broadcasting equipment, and fuelwood.
To further bolster the trading sector and improve the business environment within the regions, The Vietnam-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (VJEPA) was brought into action in 2009. As per the agreement, Vietnam will strive to eliminate 90.64% of the tariff lines.
10. Vietnam and India under ASEAN (AIFTA)
In 2003, the Leaders of ASEAN and India signed the ASEAN-India Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation. The agreement also laid a solid foundation for establishing the ASEAN-India Regional Trade and Investment Area (RTIA).
According to WTOcenter, ASEAN and India signed the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods (TIG) Agreement in 2009, which paved the way for creating one of the world’s largest FTAs. The agreement covers approximately 1.8 billion people with a combined GDP of USD 2.8 trillion. With the agreement in effect, both trading blocks shall agree to deliver on the following terms:
- Tariff liberalization of over 90% of products traded between the two Asian nations
- Elimination of tariffs on over 4,000 product lines
11. Vietnam – Eurasian Economic Union (VN-EAEU FTA)
Vietnamese enterprises now have access to a market of 181,000,000 new customers in Eurasia due to the ratification of the Free Trade Agreement between Vietnam and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), which consists of Russia, Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan.
According to data from the General Department of Customs, Vietnam exported 323.26 million USD worth of agricultural, forestry, and fishery products to the Russian market in the first seven months of 2021, an increase of 34.2% over last year. Additionally, according to the WTO, the export turnover for aquatic products, as well as agricultural products, grew by more than 50% over the same period last year.
On the other hand, in 2020, Russia exported coal briquettes, hot-rolled iron, and pork meat worth USD 1.78 billion to Vietnam.
Vietnam intends to open the market for around 90% of its total tariff lines as part of its 10-year reduction plan. The VN-EAEU FTA requires both trading blocs to agree to the following conditions for delivery:
- removal of tariffs on goods that were prioritized by the EAEU at the time of their entry into force (EIF), such as agricultural commodities
- After three to five years since the EIF, tariffs on processed meat and fish, electrical equipment, and agricultural machinery have all been eliminated.
- tariffs on chicken and pork have been eliminated five years after the EIF.
- Elimination of tariffs on automobiles and alcoholic beverages after ten years after the EIF
Source: WTOcenter
12. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)a
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is the name given to a newly formed free trade agreement among countries that include Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. China had a major role in negotiating this deal, which went into force on January 1st, 2022. It is regarded as the largest FTA in the world because it includes approximately 30% of the world’s population.
As far as Vietnam is concerned, RCEP is expected to give the agricultural industry a big boost, as it simplifies the process of entering the Chinese market (one of the biggest consumer markets in the world) as well as reducing tariffs. However, as this agreement just came into effect three months before this article was published, there is little data to examine for the time being on the actual results of the FTA.
13. Vietnam – Cuba Trade Agreement
Vietnam and Cuba have had close relations for some time now, as old communist partners. Signed in 2018, The Vietnam-Cuba Trade Agreement includes a big focus on regulations on rules of origin, trade in goods, trade defense, and technical regulations.
As per the agreement, both sides have started the process of completely removing or reducing taxes for all the products that are imported from each other’s respective markets.
14. Vietnam-Chile Free Trade Agreement (VCFTA)
Vietnam and Chile signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in 2011 under the auspices of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) conference.
The two nations will gain the following advantages from the deal.
- While the remaining products will profit from the FTA, 73% of Chilean exports will gain from tariff-free access to Vietnam. Only 4% of products will be exempt, though.
- Additionally, 75% of Vietnam’s exports would be able to enter Chile duty-free, and the remaining 25% will receive tax breaks for a period of 6 to 11 years.
15. ASEAN – Hong Kong, China Free Trade Agreement (AHKFTA)
The ASEAN – Hong Kong – China Free Trade Agreement (AHKFTA) took effect on June 11, 2019, for Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Singapore, and Thailand. The main goal is to encourage the development of the economy, boost trade and investment, and create stronger economic connections between Hong Kong and the ASEAN nations.
The agreement, which was agreed upon and signed to lower taxation, improve economic collaboration, and increase investment between Hong Kong and the regional markets in the ASEAN zones, was built upon the already solid economic basis between the two parties. The aim of Hong Kong to increase its business possibilities in Vietnam will also help compensate for the escalating US-China trade war.
Upcoming Free Trade Agreements
Apart from the FTAs explained in the article, Vietnam is also part of many planned future agreements, some of which are a result of its ASEAN membership. Three FTAs are already in negotiations between participants, and eight more have been proposed for future discussions. Most notably, talks for a free trade agreement between Israel and Vietnam began in 2015. Additionally, some sort of trade accords has been a common topic of Vietnam-Pakistan and Vietnam-Ukraine meetings as well.
If all of these plans are to be executed, Vietnam will be an official signatory of a total of 27 past, present, and future free trade agreements.
About Us
Cekindo Vietnam is part of InCorp Group, based in Singapore. Incorp is the largest corporate service provider in the APAC Region. We assist foreign companies with their market entry needs in Vietnam, including Company Registration, Accounting & Taxes, HR & Payroll, Product Registration, Employment of Record, and other services.
